To answer that question, I’ll need to explain a part of the brain called the Limbic System.
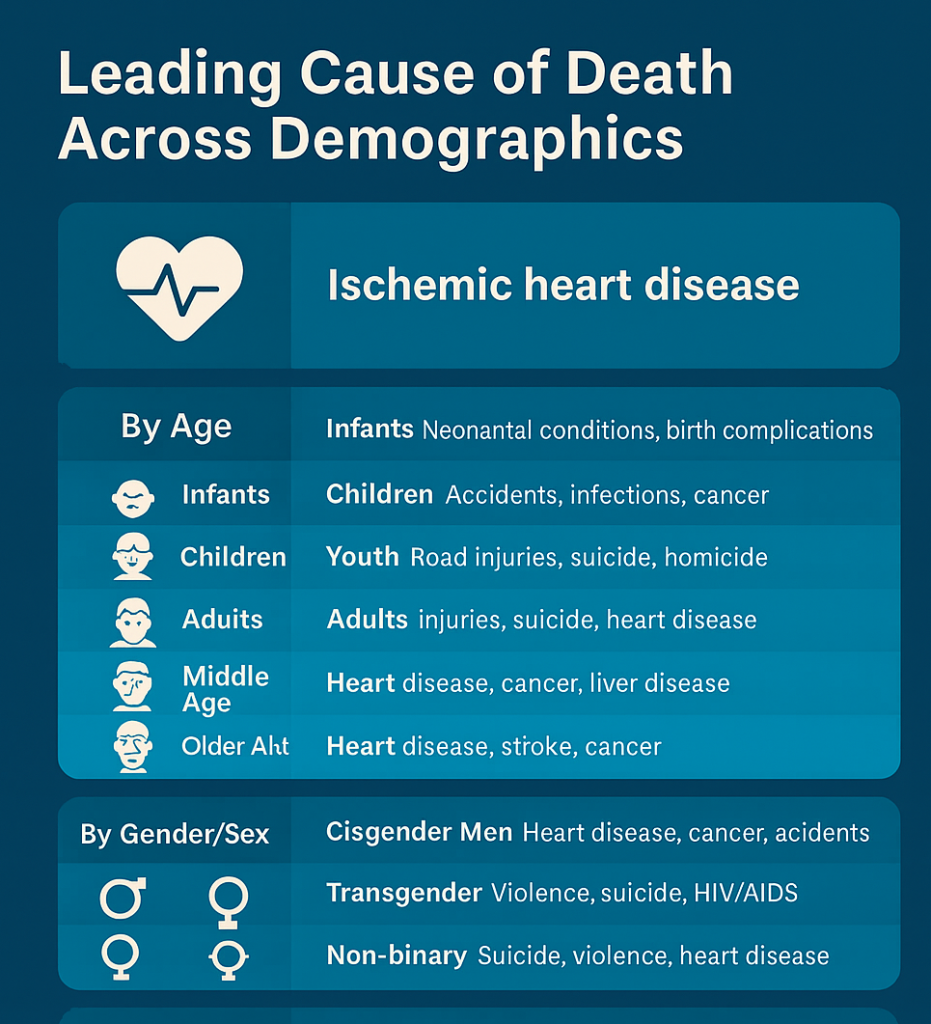
Within the brain there is a set of structures called the limbic system. There are several important structures within the limbic system: the amygdala, hippocampus, thalamus, hypothalamus, basal ganglia, and cingulate gyrus. The limbic system is among the oldest parts of the brain in evolutionary terms. It’s not just found in humans and other mammals, but also fish, amphibians, and reptiles.
The limbic system is the part of the brain involved in our behavioural and emotional responses, especially when it comes to behaviours we need for survival: feeding, reproduction and caring for our young, and fight or flight responses (https://qbi.uq.edu.au/brain/brain-anatomy/limbic-system).
The limbic system contains the brain’s reward circuit or pathway. The reward circuit links together several brain structures that control and regulate our ability to feel pleasure (or “reward”). The sensation of pleasure or reward motivates us to repeat behaviours. When the reward circuit is activated, each individual neuron (nerve cell) in the circuit relays electrical and chemical signals.
In a healthy world without addictive manufactured drugs, humans survive and thrive when they are rewarded for certain behaviours (cleaning, hard work, sex, eating, achieving goals etc), hence evolution has provided us with this feel-good chemical so that we will repeat pleasurable behaviours.
There is a gap between neurons called the synapse. Neurons communicate with each other by sending an electro-chemical signal from one neuron (pre-synaptic neuron) to the next (post-synaptic neuron). In the reward circuit, neurons release several neurotransmitters (chemical messengers). One of these is called dopamine. Released dopamine molecules travel across the synapse and link up with proteins called dopamine receptors on the surface of the post-synaptic neuron (the receiving nerve cell). When the dopamine binds to the dopamine receptor, it causes proteins attached to the interior part of the post-synaptic neuron to carry the signal onward within the cell. Some dopamine will re-enter the pre-synaptic nerve cell via dopamine transporters, and it can be re-released.
When a reward is encountered, the pre-synaptic nerve cell (neuron) releases a large amount of dopamine in a rapid burst. Dopamine transporters will remove “excessive” amounts of dopamine naturally within the limbic system. Dopamine surges like this help the brain to learn and adapt to a complex social and physical world.
Drugs like methamphetamine (a stimulant drug) are able to “hijack” this process contributing to behaviours which can be considered unnatural or potentially dysfunctional. A range of consequences can follow.
When someone uses methamphetamine, the drug quickly enters the brain, depending on how the drug is administered. Nevertheless, meth or ice is quick acting. Meth blocks the re-entry of dopamine back into the pre-synaptic neuron – which is not what happens naturally. This is also what cocaine does to the brain. However, unlike cocaine, higher doses of meth increase the release of dopamine from the presynaptic neuron leading to a significantly greater amount of dopamine within the synapse. Higher doses of cocaine will not release “more dopamine” from the pre-synaptic neuron like meth does. This is why after about 30 minutes or so, people who use cocaine will need more to maintain the high.
Dopamine gets trapped in the synapse (space between nerve cells) because the meth (like cocaine) prevents “transporters” from removing it back into the cell it came from. The postsynaptic cell is activated to dangerously high levels as it absorbs so much dopamine over a long period of time. The person using meth experiences powerful feelings of euphoria, increased energy, wakefulness, physical activity, and a decreased appetite.
When an unnatural amount of dopamine floods the limbic system like this over a long period of time, without reabsorption, then our brain is not replenished with dopamine, hence people who use meth often (even on a single occasion) may feel unmotivated, depressed, joyless, and/or pointlessness when they stop using. Figuratively speaking, the brain is “empty” or low on dopamine fuel, and it will take time to for dopamine to return to baseline levels and replenish itself. This may motivate the user to seek more methamphetamine to return to “normal”.
Methamphetamine can also cause a variety of cardiovascular problems, including rapid heart rate, irregular heartbeat, and increased blood pressure. Hyperthermia (elevated body temperature) and convulsions may occur with methamphetamine overdose, and if not treated immediately, can result in death (What are the immediate (short-term) effects of methamphetamine misuse? | National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) (nih.gov))
SIGNS OF SUBSTANCE MISUSE OR ADDICTION
- Finding it difficult to meet responsibilities.
- Withdrawing from activities or not enjoying activities that used to provide satisfaction e.g. work, family, hobbies, sports, socialising.
- Taking part in more dangerous or risky behaviours e.g., drink driving, unprotected sex, using dirty needles, criminal behaviour.
- Behaviour changes e.g., stealing, exhibiting violence behaviour toward others.
- Conflict with partner/family/friends, losing friends.
- Experiencing signs of depression, anxiety, paranoia, or psychosis.
- Needing more substance to experience the same effects
- Cravings and urges to use the substance and symptoms of withdrawal when not using the substance.
- Having difficulty reducing or stopping substance use.
- Regretting behaviours while under the influence and continuing to use again.
(Substance abuse, misuse and addiction | Lifeline Australia | 13 11 14)